Understanding CISSP Domain 7, Security Operations - Part 4
Security Operations is the practical application of security concepts to identify, investigate, and mitigate risks across an organization's daily activities and operational lifecycle.
Part 1 covered important concepts, including investigations, evidence collection, logging and monitoring, threat intelligence, and configuration management.
We continued exploring areas such as resource protection, incident response, and detection and preventive technologies in Part 2.
In Part 3, we looked at vulnerability and patch management, change management, and disaster recovery plans, processes, and testing.
In the last article, we’ll discuss business continuity planning and physical and personnel safety.
Let’s dive into the domain and cover the material by following the ISC2 exam outline.
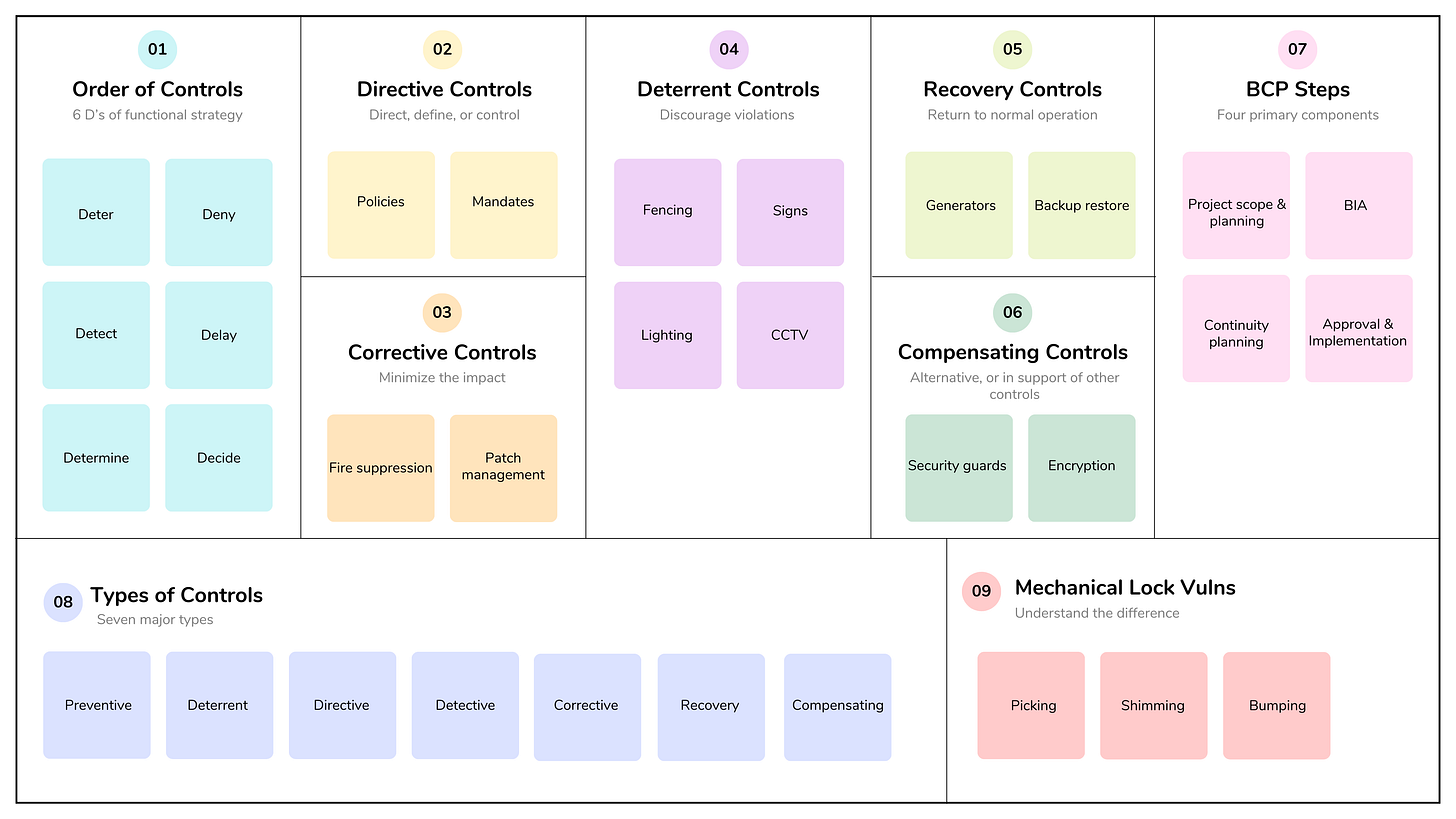
7.13 - Participate in Business Continuity (BC) planning and exercises
Business Continuity Management (BCM) is the holistic process that identifies potential threats and risks to operational continuity and provides a framework for building resilience. It ensures an organization can continue to deliver products or services at acceptable, predefined levels during and after a disruption.
The BCM process drives disaster planning and preparation by conducting the Business Impact Analysis (BIA). The BIA helps define metrics (e.g., RPO, RTO, WRT, and MTD) that, in turn, drive the creation of Business Continuity Plans (BCPs) and Disaster Recovery Plans (DRPs). BCM primarily aims to ensure an organization's survival during a disaster by maintaining its most critical processes.
Metrics that you should be familiar with: